Punjab Boundary Length: Punjab, located in the northern region of India, has a boundary length of approximately 1,817 kilometers, making it a crucial state geographically and strategically. Its borders are shared with Pakistan to the west and three Indian states: Haryana, Rajasthan, and Himachal Pradesh.
Table of Contents
Punjab Boundary Length: The Land of Five Rivers
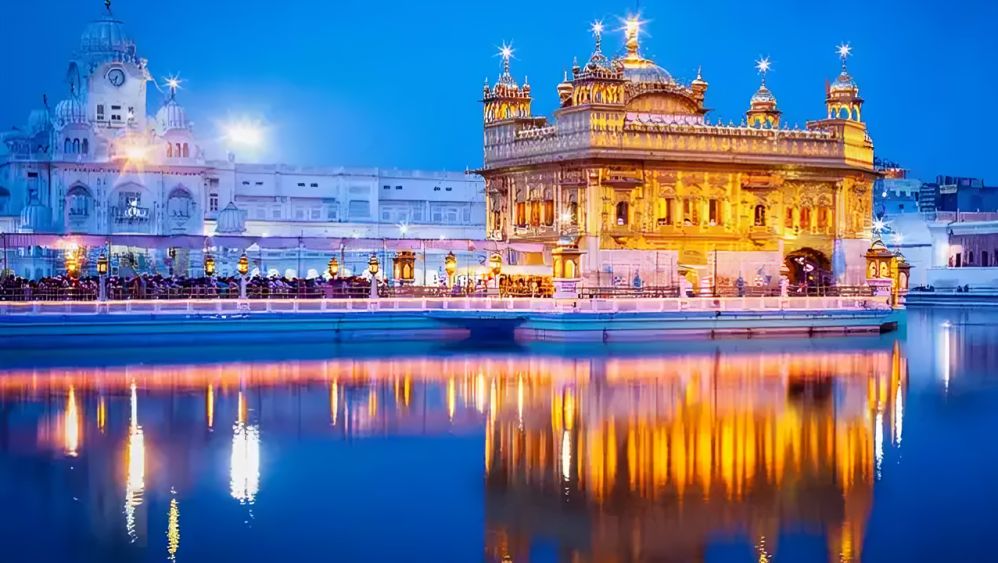

Punjab, derived from the Persian words “Panj” (five) and “Ab” (water), means “Land of Five Rivers.” Located in northern India, Punjab is one of the most prosperous and culturally rich states in the country. Known for its fertile lands, vibrant traditions, and historical significance, Punjab is a cornerstone of India’s agricultural and cultural landscape.
Geography and Borders
- Total Area: Approximately 50,362 square kilometers.
- Bordering States: Punjab shares boundaries with Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, and Rajasthan, and an international border with Pakistan.
- The Indus River basin and its tributaries, including Sutlej, Beas, and Ravi, make Punjab one of the most agriculturally productive regions in the world.
International Border with Pakistan
Length: 553 kilometers.
This boundary is marked by the Radcliffe Line, established during the partition of India in 1947. The Wagah-Attari border is the most prominent crossing point, known for its ceremonial flag-lowering event that attracts tourists. This region has significant historical and cultural importance and remains a sensitive area due to geopolitical tensions.
Inter-State Borders
- Haryana (374 kilometers):
- Lies to Punjab’s southeast and is integral to economic and transport connections.
- Shared borders are vital for trade and workforce movement between the two states.
- Rajasthan (89 kilometers):
- Located to the southwest, Rajasthan shares a smaller border with Punjab near the arid zones of the state.
- The area is part of Punjab’s Malwa region and has limited agricultural activity compared to the rest of Punjab.
- Himachal Pradesh (672 kilometers):
- Forms the northeastern boundary of Punjab and is characterized by hilly terrain.
- This border plays a significant role in cultural exchange and tourism.
- The rivers Sutlej and Beas flow through this region, contributing to Punjab’s irrigation system.
Strategic and Economic Importance

Punjab’s border with Pakistan is both an opportunity for trade (via Wagah-Attari) and a region of military focus. The fertile lands along its inter-state borders with Haryana and Himachal Pradesh ensure Punjab’s position as India’s breadbasket, producing significant quantities of wheat and rice. The shorter border with Rajasthan connects Punjab to western India, facilitating transport and cultural ties.
Cultural Richness
Punjab is the birthplace of Sikhism, and the Golden Temple (Harmandir Sahib) in Amritsar is its most revered site. Festivals like Baisakhi, Lohri, and Gurpurab are celebrated with unmatched enthusiasm. The state is also renowned for its Punjabi music, Bhangra dance, and delicious cuisine, including makki di roti and sarson da saag.
Economy
Known as India’s breadbasket, Punjab contributes significantly to the nation’s food grain supply, particularly wheat and rice. The Green Revolution began here, transforming India’s agricultural landscape. Industrial hubs like Ludhiana are also known for manufacturing, particularly textiles and bicycles.
Historical Importance

Punjab has been a witness to several historical events, including the rise of the Sikh Empire, the partition of India in 1947, and key battles of Indian independence. Its rich heritage is reflected in sites like Jallianwala Bagh, Qila Mubarak, and ancient forts and monuments.
Modern Punjab
Today, Punjab is a blend of tradition and modernity, with urban centers like Chandigarh, Amritsar, and Ludhiana coexisting alongside vibrant rural areas. Its progressive outlook, strong cultural identity, and hardworking people continue to make Punjab a vital part of India’s growth story.













