Unlike many sports, cricket grounds lack standardized dimensions, allowing for unique features such as the 2.5-meter slope at Lord’s Cricket Ground. Typically, the diameter ranges from 140 to 150 meters (450–500 feet) for men’s cricket and 110 to 130 meters (360–420 feet) for women’s cricket.
From boundary ropes to pitch design, every element influences the game. Here’s a closer look at cricket boundary dimensions:
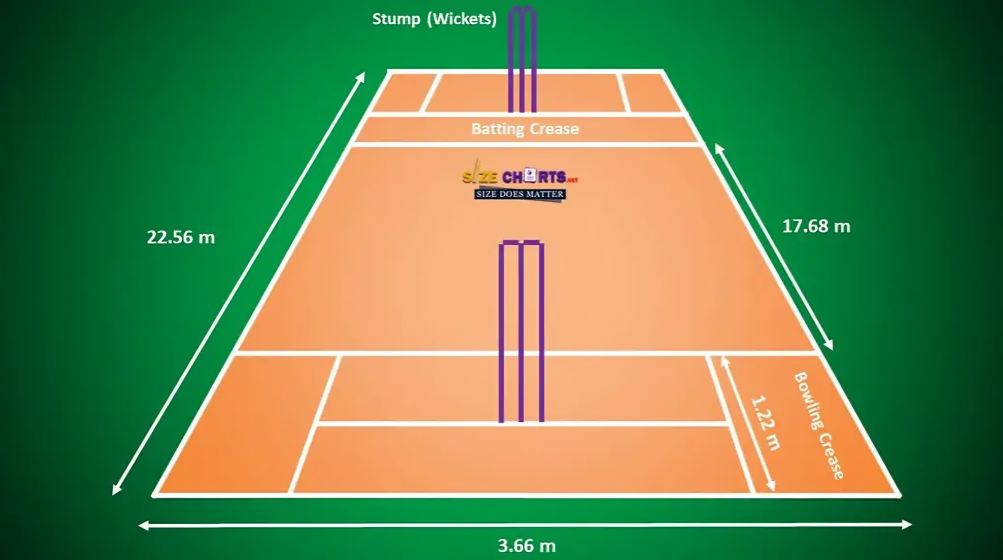
Pitch Dimensions of Cricket Boundary Ground
Cricket Boundary Ground: At the center of every cricket ground is the pitch, where batsmen face bowlers in their quest to score runs, while fielders aim to dismiss them by targeting the stumps.
Each end of the pitch features three stumps topped with two bails, forming a wicket. The batsman stands at the batting end, while the bowler delivers from the opposite end.
Creases, marked lines on the pitch, play a vital role by defining batsmen’s safe zones and ensuring deliveries are legitimate. These markings are also instrumental in determining dismissals.
The central “danger area,” a 2-foot-wide rectangle starting 5 feet from each popping crease, must remain untouched by bowlers during their follow-through to maintain the integrity of the surface, as mandated by cricket’s laws.
Cricket Boundary Ground Rope Dimensions

Cricket Boundary Ground: The ICC Standard Playing Conditions, outlined in Law 19.1.3 of the ICC Men’s Test and ODI Playing Conditions, define the permissible dimensions for boundary ropes in international cricket.
Boundaries should maximize the playing area, with no boundary exceeding 90 yards (82 meters) and none shorter than 65 yards (59 meters) from the pitch’s center. Additionally, a minimum three-yard gap must separate the boundary rope from fencing or advertising boards to ensure player safety during dives.
Boundary sizes often vary based on the game format. T20s typically feature shorter boundaries to encourage aggressive batting, while Test matches emphasize larger boundaries, prioritizing strategic shot-making and running between the wickets.
List of Largest Cricket Boundary Grounds Based On Size
| No. | Ground Name | Country | Boundary size in metres |
| 1 | Sydney Cricket Ground (SCG) | Australia | 93.72 |
| 2 | Lords, London | England | 88.87 |
| 3 | The Wanderers, Johannesburg | South Africa | 86.76 |
| 4 | Melbourne Cricket Ground (MCG) | Australia | 86.24 |
| 5 | SSC Colombo | Sri Lanka | 86.09 |
Cricket Boundary Ground Size in T20 Matches
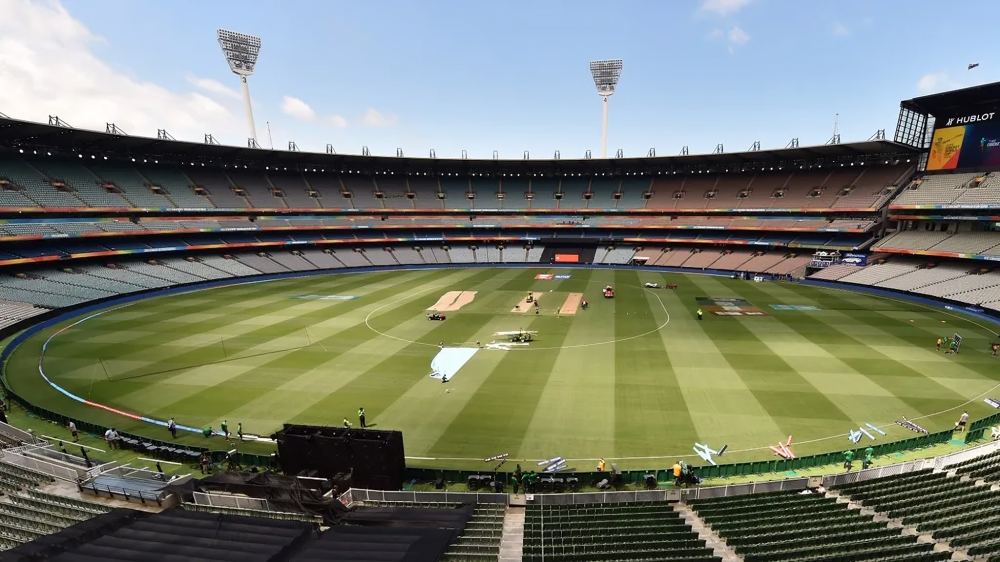

In T20 cricket, grounds feature shorter boundaries than in Test or ODI matches to encourage aggressive batting, resulting in more sixes and higher scores, enhancing the game’s excitement. While the pitch dimensions remain standard at 22 yards (20.12 meters) long and 10 feet (3.05 meters) wide, boundary distances vary by venue. Boundaries must fall within 65 to 90 yards from the pitch’s center, adhering to ICC regulations.
Cricket Ground Size in Women’s T20s
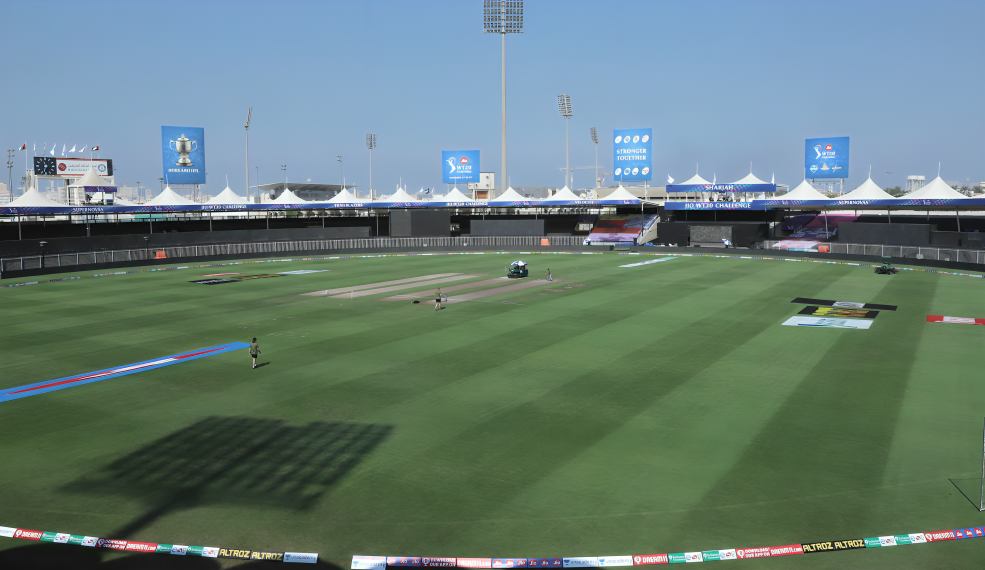

According to the ICC playing conditions for women’s T20 cricket, the boundary must be between 60 yards (54.86 meters) and 70 yards (64 meters) from the center of the pitch. However, grounds that do not meet the minimum boundary requirement but are already approved for international cricket will not lose their hosting rights. In such cases, the boundary will be adjusted to optimize the playing area size.













