Exploring Total Boundary Lengths of Worldwide. Continents vary greatly in their boundary lengths due to their size, geography, and coastlines. Europe leads with 87,200 km, thanks to its irregular coastline. Asia follows at 62,800 km, driven by vast land borders. North America and Oceania feature extensive coastlines, while Africa’s compact shape limits its total to 26,000 km. Antarctica’s boundary is purely oceanic at 17,968 km.
1. Asia
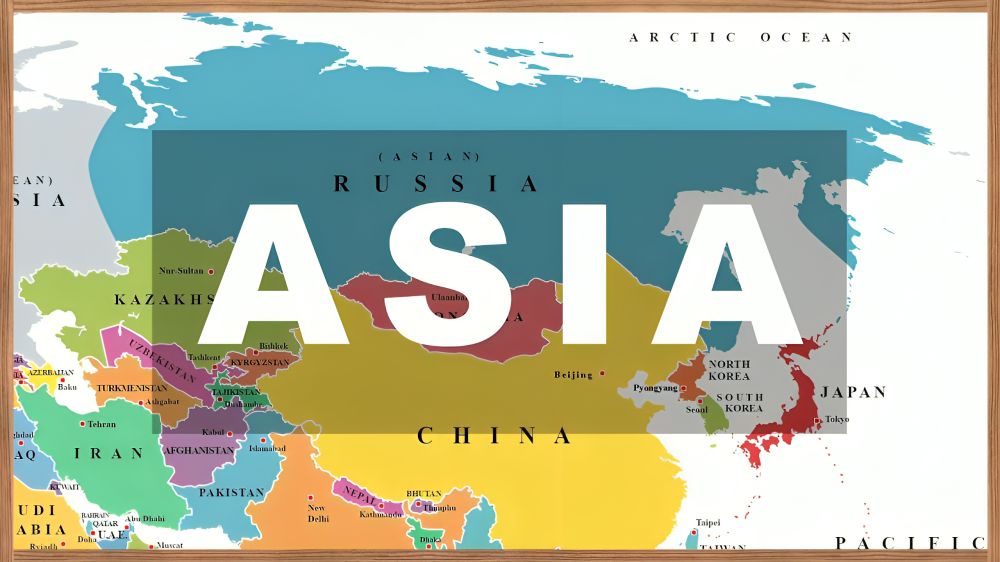
Asia, the largest continent, boasts a total boundary length of approximately 62,800 kilometers, making it the most extensive among all continents. This includes both land borders and coastlines. Its land boundaries are shared with numerous countries, reflecting Asia’s diversity and complex geopolitical landscape. The continent’s borders stretch across Europe, the Middle East, and connect to other major regions. Additionally, Asia’s expansive coastlines along the Pacific, Indian, and Arctic Oceans significantly contribute to its total boundary length. These natural and political boundaries define Asia’s immense geographical diversity, from towering mountains to sprawling seas, highlighting its global significance.
2. Africa
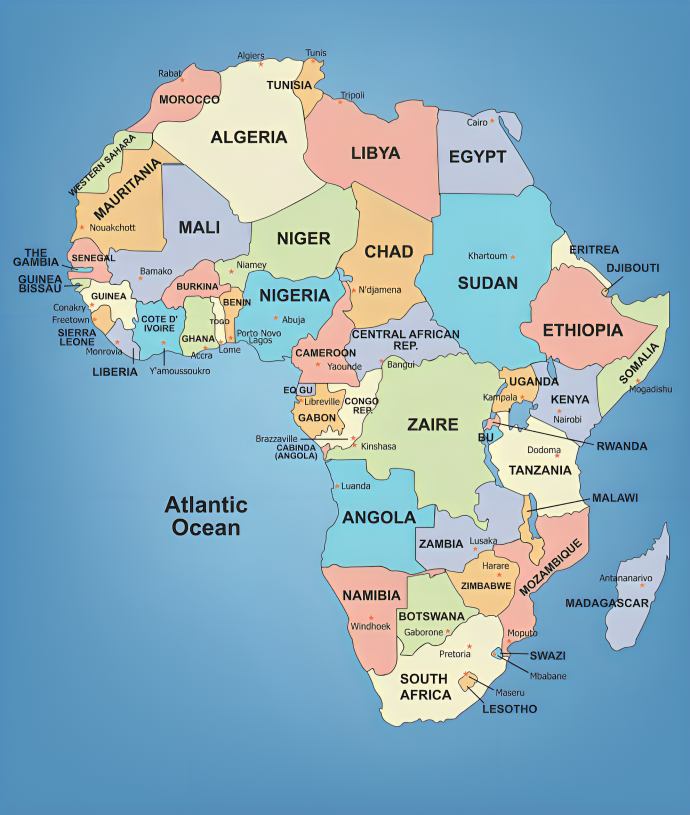

Africa’s total boundary length is approximately 26,000 kilometers, encompassing both land borders and coastlines. Despite being the second-largest continent, Africa’s coastlines are relatively shorter compared to its vast size, attributed to its compact and rounded landmass. The continent is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the Indian Ocean to the east. Its 54 countries share diverse land borders, featuring deserts, mountains, rivers, and forests. The intricate borders reflect Africa’s cultural and geographical diversity, making it a region of immense ecological and geopolitical significance.
3. North America
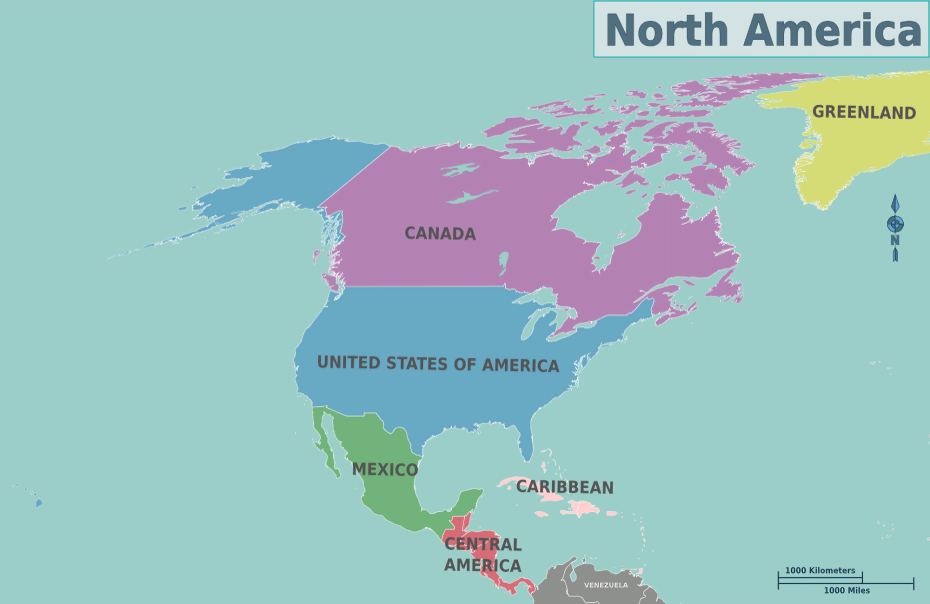
Total Boundary Length: Approximately 60,000 kilometers.
North America’s boundary length includes the land borders of Canada, the United States, Mexico, and the nations of Central America, alongside extensive coastlines along the Arctic, Atlantic, and Pacific Oceans. The USA-Canada border, stretching over 8,891 kilometers, is the longest international land border in the world. These vast boundaries encompass diverse geographical features such as mountains, rivers, and plains. The Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea also add to North America’s coastline, making it one of the most geographically diverse continents. These borders play a crucial role in trade, migration, and cultural exchange across the region.
4. South America
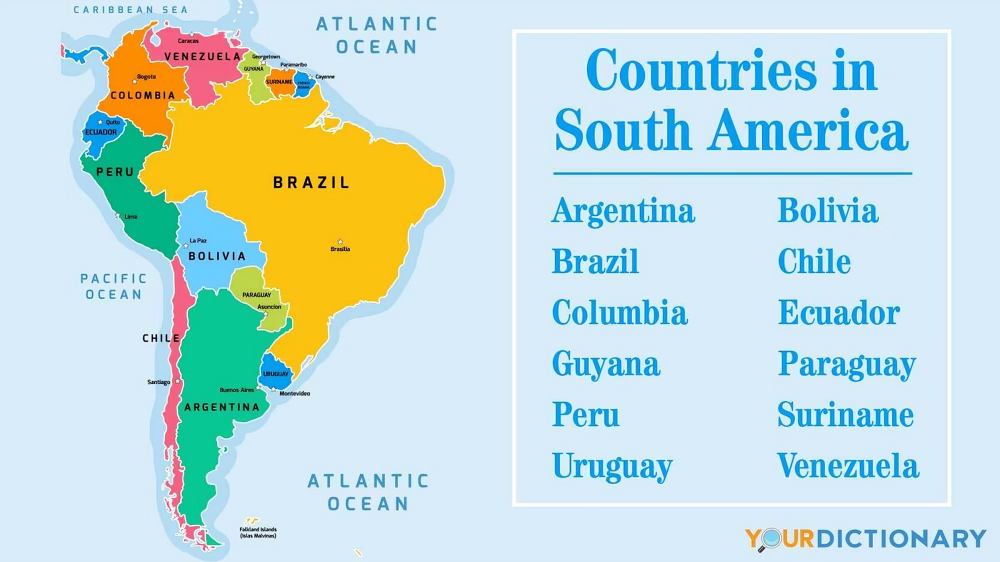
Total Boundary Length: Approximately 28,700 kilometers
South America boasts diverse geographical features, with boundaries encompassing land borders between 12 countries and extensive coastlines along the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Brazil, the largest country on the continent, significantly contributes to the total boundary length with its vast landmass and over 7,000 kilometers of coastline. Other countries like Argentina, Chile, and Peru also add to the length with their lengthy coastal stretches. The Andes Mountains, Amazon Rainforest, and numerous rivers create natural borders, highlighting the continent’s rich geographical and cultural diversity. These boundaries connect and define the vibrant nations of South America.
5. Europe
Total Boundary Length: Approximately 87,200 kilometers
Europe is known for its complex and extensive network of political boundaries, with 44 countries in total. The continent’s coastline, highly irregular due to numerous peninsulas, bays, and islands, contributes significantly to the overall boundary length. Countries like Norway, Greece, and Italy are particularly notable for their jagged coastlines, adding to Europe’s boundary measurements. Additionally, Europe’s borders are shaped by both historical divisions and modern geopolitical factors, with some countries sharing land boundaries and others marked by water bodies. This intricate geography makes Europe one of the most diverse and politically complex continents in the world.
6. Australia (Including Oceania)
Total Boundary Length: Approximately 59,600 kilometers
Australia, the world’s smallest continent, includes not only the Australian mainland but also thousands of islands spread across the Pacific and Indian Oceans. Due to its insular nature, Australia has no significant land borders with other countries, making its boundaries primarily coastline. The long coastline stretches across the southern, eastern, and western shores, contributing to the vast boundary length. Oceania, which encompasses Australia and numerous island nations, adds to the total length, with many island nations like Papua New Guinea and Fiji contributing to the region’s intricate boundaries and diverse geography.
7. Antarctica
Total Boundary Length: Approximately 17,968 kilometers.
Antarctica, the southernmost continent, is entirely surrounded by the Southern Ocean, with no land borders or neighboring countries. Its boundary length consists of a continuous coastline that stretches over 17,900 kilometers. The continent is uninhabited, with no permanent settlements, and is governed by the Antarctic Treaty System, which prohibits military activity and mineral exploitation. Antarctica is primarily a scientific preserve, with research stations operated by various countries. The harsh, frozen environment and remote location make it one of the most unique and least explored regions on Earth.
Summary Table
| Continent | Total Boundary Length (Approx.) |
|---|---|
| Asia | 62,800 km |
| Africa | 26,000 km |
| North America | 60,000 km |
| South America | 28,700 km |
| Europe | 87,200 km |
| Australia/Oceania | 59,600 km |
| Antarctica | 17,968 km |
Key Notes:
- Europe has the highest boundary length, primarily due to its complex coastline.
- Asia ranks second because of its vast landmass and political divisions.
- Antarctica has the shortest boundary, with no land borders and a consistent coastline.












